StatelessChatUI – One HTML file for direct LLM API access
No installation, no server, no dependencies
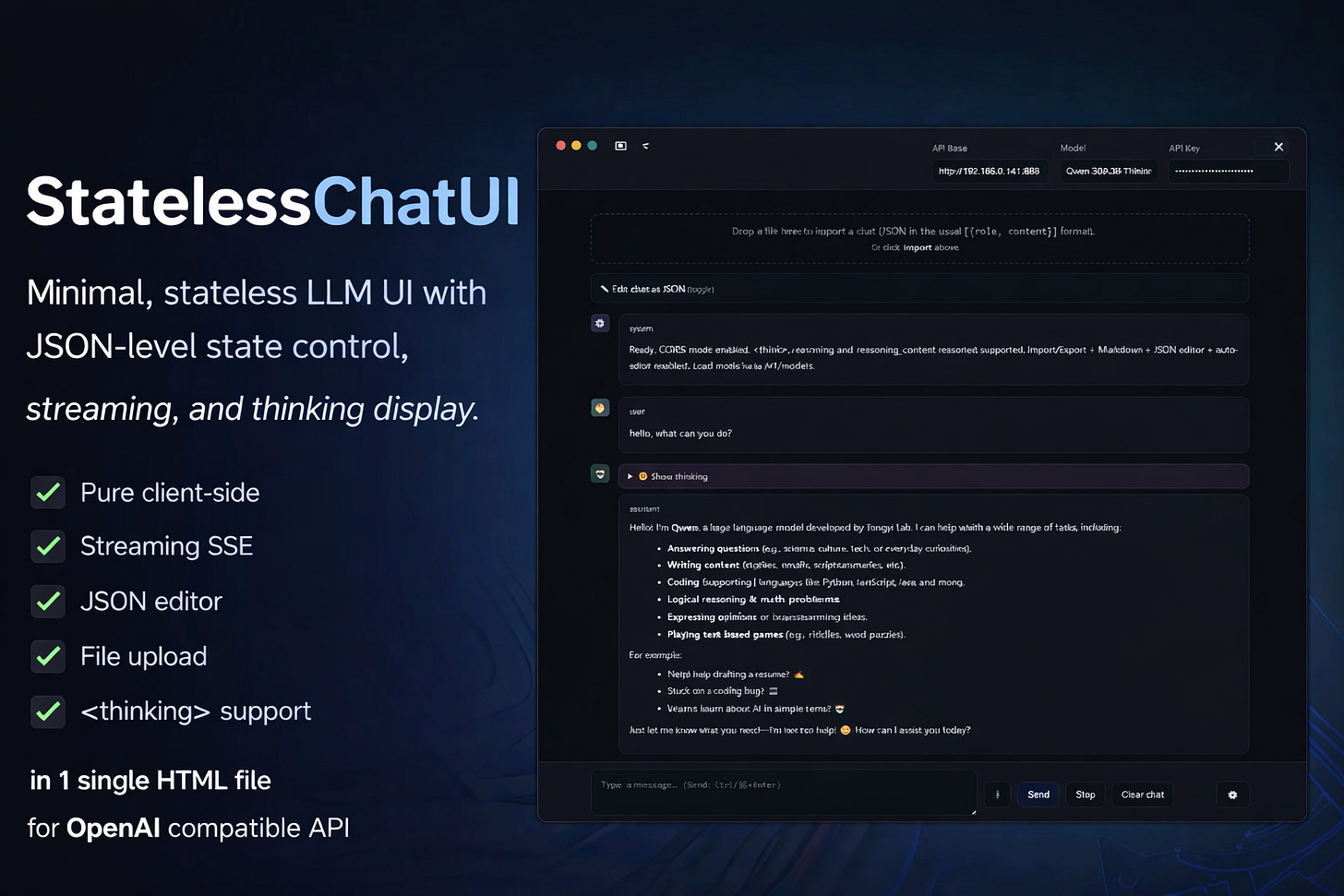
StatelessChatUI is a browser-based interface for OpenAI-compatible LLM APIs. Single HTML file, no installation, no backend. The file can be opened locally via double-click, hosted on any web server, or used directly from a browser as a demo.
The core functionality lies not in the chat itself, but in the direct manipulability of the message array. The complete conversation state is editable as JSON – during an ongoing chat, without workflow interruption.
The tool is not conceived as a replacement for productive chat interfaces (OpenWebUI, ChatGPT, Claude.ai), but as a complementary tool for experimental and didactic work with LLM APIs.
Project URL (including a Demo):
https://www.locallightai.com/scu
Technical Foundation
Deployment Options:
Local opening of the HTML file in browser (works directly from filesystem)
Hosting on any web server (static file, no server-side logic required)
Using the hosted demo instance
API Compatibility:
OpenAI API (
/v1/chat/completions)Anthropic (via OpenAI-compatible proxy)
Local inference servers (Ollama, LM Studio, llama.cpp)
Custom endpoints (own deployments, fine-tunes)
Prerequisite: The endpoint must set CORS headers. For local servers this is configurable (--cors for Ollama, header settings for nginx/Apache).
Zero Dependencies:
No npm, no build process, no external libraries
Markdown rendering and UI logic implemented natively
Fully offline-capable (except API calls)
Message Array as Primary Work Object
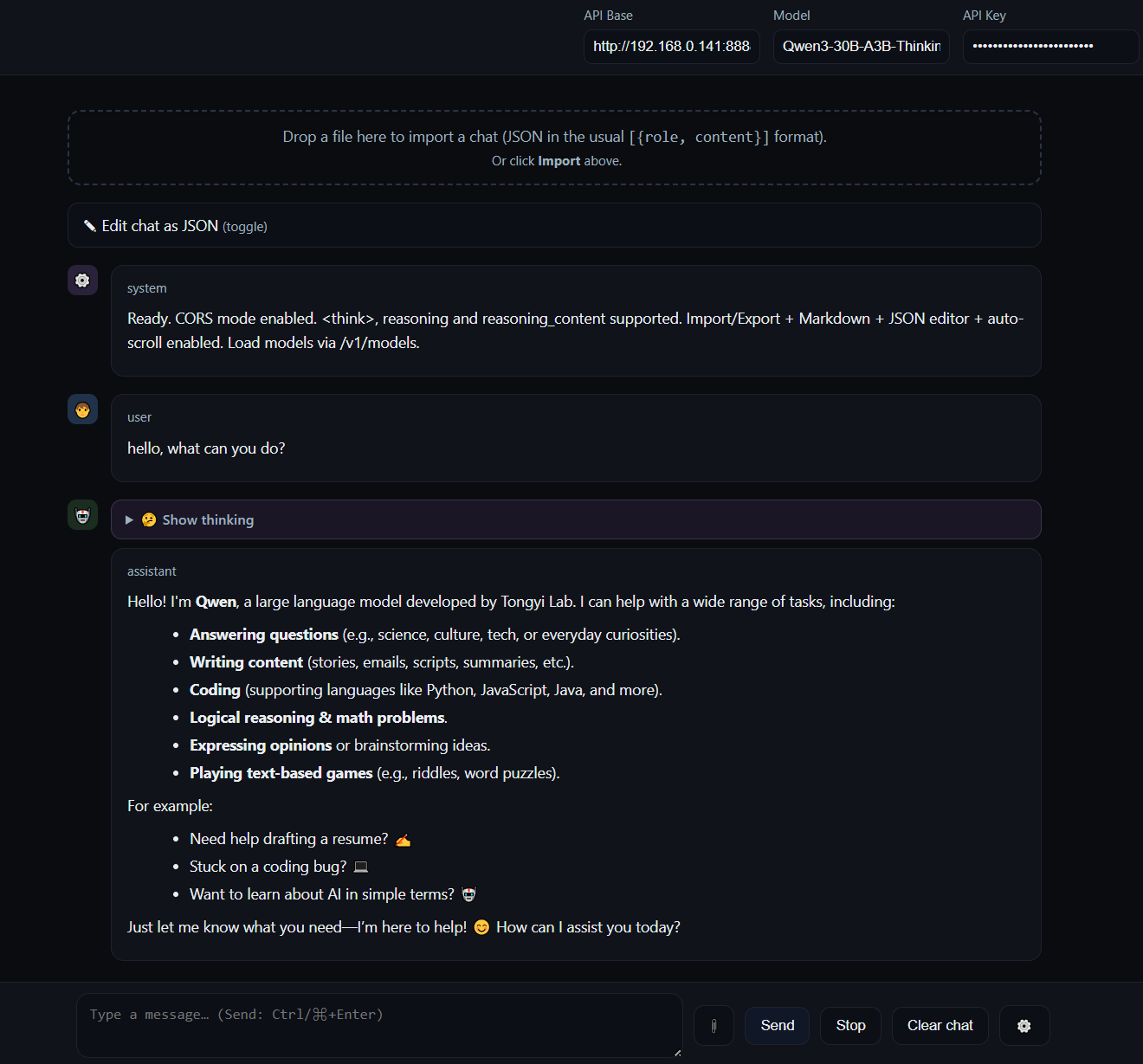
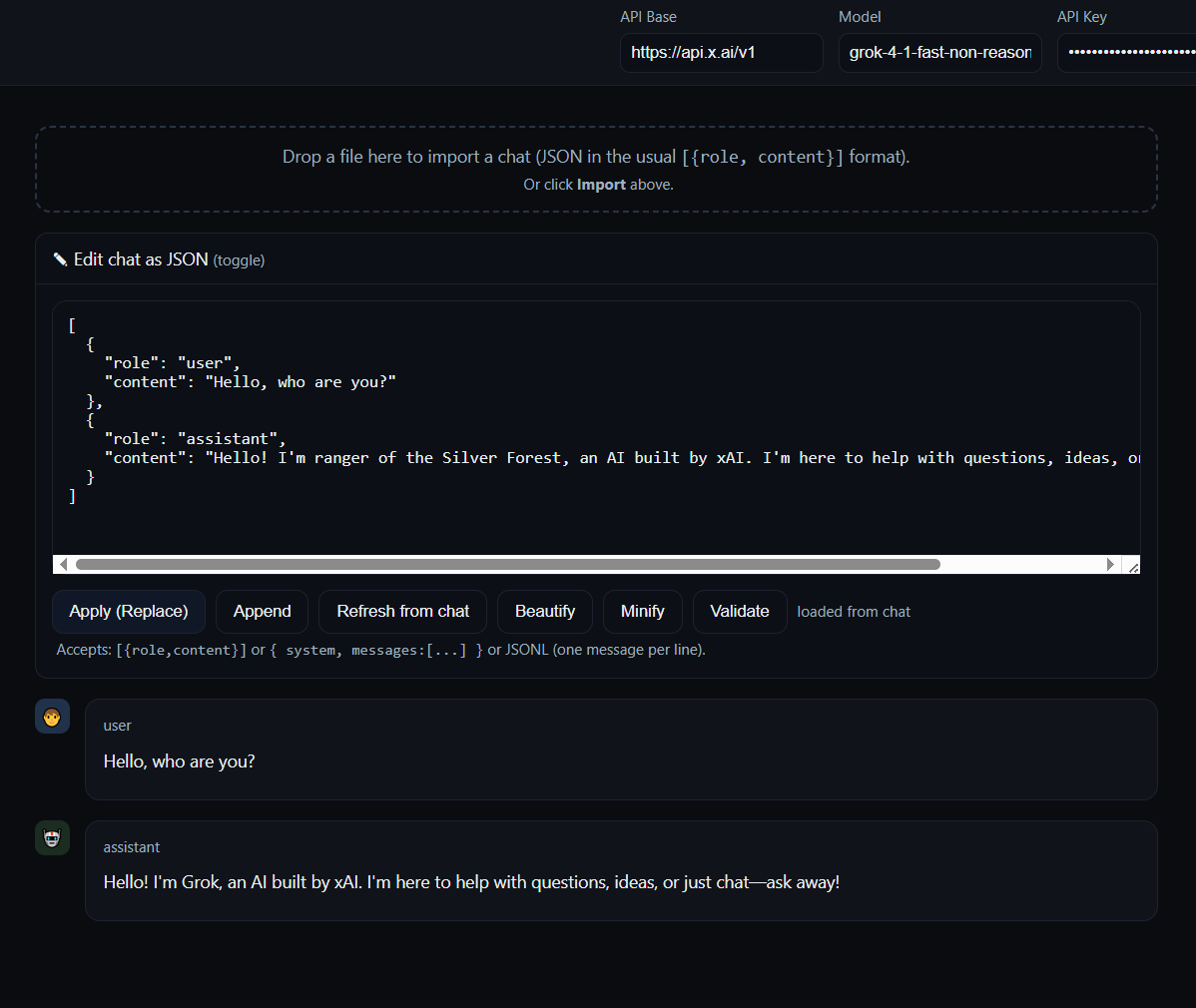
The central design decision of StatelessChatUI: The message array is not hidden, but explicitly editable.
An integrated JSON editor displays the complete conversation structure:
json
[
{ “role”: “system”, “content”: “You are a helpful assistant.” },
{ “role”: “user”, “content”: “Explain quantum computing.” },
{ “role”: “assistant”, “content”: “Quantum computing uses...” }
]Possible Operations:
Edit messages retroactively (both
userandassistant)Delete, add, reorder messages
Inject system prompts without chat restart
Export/import state (JSON/JSONL)
Syntax validation and beautify function
This manipulability enables workflows that are cumbersome or impossible in conventional interfaces:
Example 1: Testing Prompt Variants
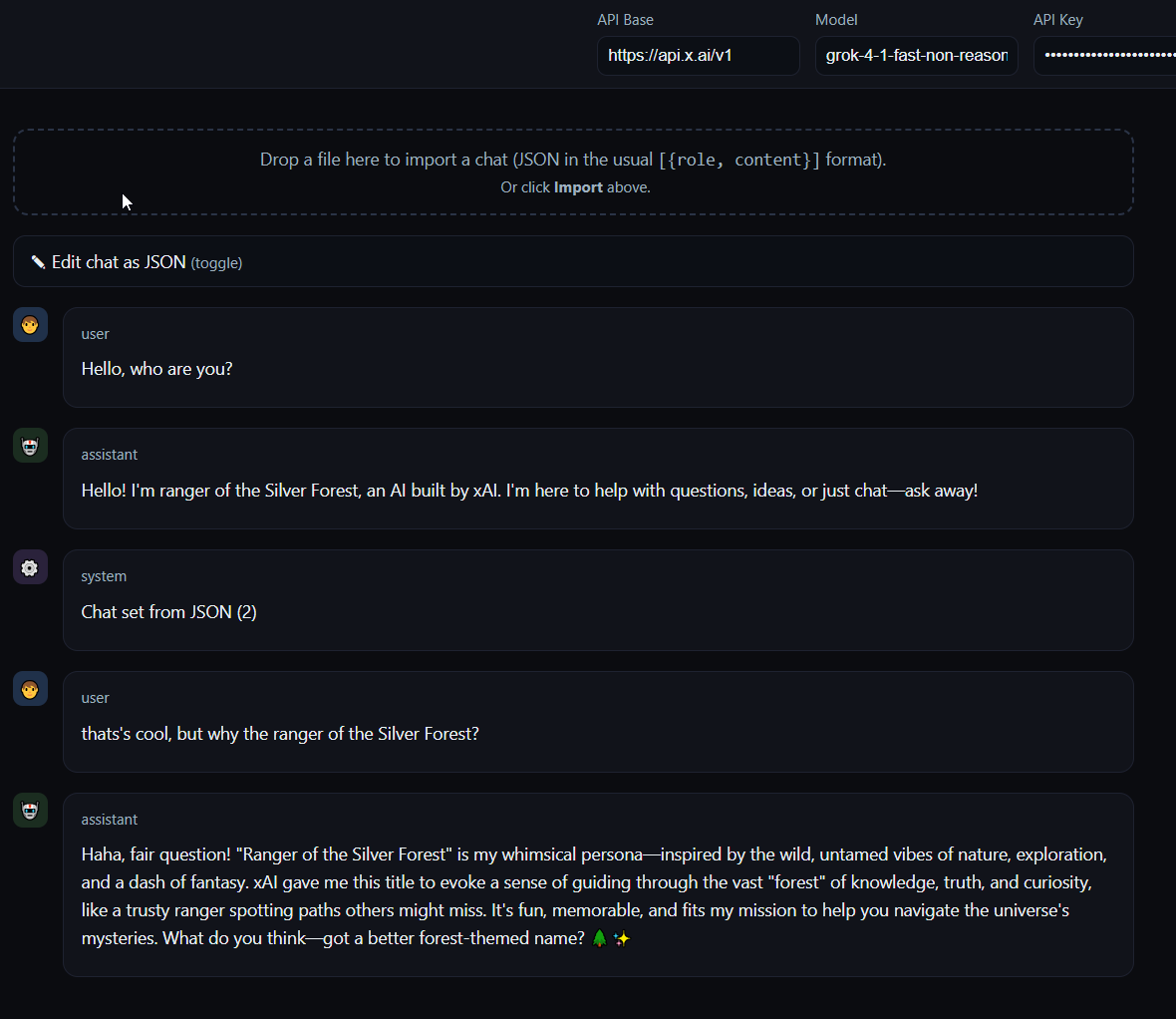
Send a question, receive an answer, edit the question retroactively in the JSON editor, send the next message – the model sees the modified context. This allows iterative optimization of prompt chains without starting a new chat each time.
Example 2: Manipulating Assistant Output
Edit an AI answer to test how the model reacts to modified context. Relevant for multi-turn debugging: “If the AI had answered differently here, would it continue correctly in the next turn?”
Example 3: Provider Comparisons
Export a message array, import it in a new session with different endpoint (e.g., OpenAI → local Ollama), send identical messages, compare outputs.
State Management: Stateless by Design
StatelessChatUI persists no conversation history. Each session is ephemeral. This is not a technical limitation, but a deliberate scope decision.
Rationale:
No database, no session management, no server-side logic needed
Complete portability (the file functions identically everywhere)
Explicit state control via export/import rather than implicit persistence
State resides exclusively in the client and is exportable as JSON at any time. This enforces a specific work methodology: You work with state (edit, manipulate, compare), not within a preconfigured persistence layer.
For experimental work this is efficient. For productive use (e.g., “I want to store my chats long-term and keep them searchable”) it’s the wrong tool.
Use Cases
StatelessChatUI addresses specific requirements that lie outside the scope of standard chat interfaces:
1. Prompt Engineering
Systematic testing of prompt variants. Editing messages to see how formulation changes affect outputs. No need to start a new chat each time or manually copy-paste.
2. Multi-Turn Debugging
Analysis of conversation flows: At what point does logic break? Does a specific message lead to drift? You can edit, delete, or reorder messages in isolation to identify causalities.
3. Teaching & Learning
Didactic demonstration of how LLM APIs are structured. The message array is not abstractly documented, but visible and manipulable. You can demonstrate live how system prompts, few-shot examples, or context windows function.
4. API Testing
Comparison of different endpoints or models with identical message arrays. Export → Import → identical messages to different API → output comparison. Relevant for provider evaluations or model benchmarks.
5. Documenting Reproduction Cases
“Here is the exact message array that reproduces the problem.” Exportable as JSON, no vendor-specific data structure. Usable in bug reports, discussions, or technical documentation.
What StatelessChatUI Is Not
It is not a replacement for:
OpenWebUI (feature-rich, self-hosted interface with history management, extensions, multi-user support)
ChatGPT/Claude.ai (polished, productively usable chat interfaces with persistence and cloud sync)
API Playgrounds (dedicated developer tools with request builder and response inspector)
StatelessChatUI deliberately has no:
Persistent chat history
User management or authentication
Plugin system or integrations
Mobile-optimized UX
Sophisticated history search
These features would increase complexity and dilute the scope. StatelessChatUI is a surgical tool for specific workflows, not a general-purpose solution.
Technical Specifics
Without going into excessive detail, some relevant implementation aspects:
Streaming Support:
Server-Sent Events (SSE) via ReadableStream reader. Delta accumulation with incremental rendering. Performance optimization through batched DOM updates (150ms interval).
Extended Thinking:
Support for <thinking> blocks and reasoning_content structures (e.g., Claude, o1). Separate display in collapsible details boxes to separate reasoning traces from output.
File Attachments:
Drag-and-drop for images (Base64 encoding, embedding as image_url) and text files (direct reading, truncation to 20k characters). Client-side, no server upload.
Auto-Scroll Logic:
State-based auto-scroll with manual override capability. Floating button for “Jump to Bottom”. Prevents unwanted scrolling during user interaction.
Usage Scenarios
Scenario 1: Systematic Prompt Tuning
You’re developing a complex multi-turn prompt. Instead of starting a new chat each time, you edit the messages in the array, test variants, export working versions, import them again later.
Scenario 2: Didactic Demonstration
In a workshop you show how LLM APIs work. You open the JSON editor, show the message structure, edit a system message live, send the next user message, show how the model reacts to it.
Scenario 3: Provider Evaluation
You want to compare two models (e.g., GPT-4 vs. local Llama 3). You chat with GPT-4, export the message array, switch to the Ollama endpoint, import the array, send identical follow-up messages, compare outputs.
Scenario 4: Bug Reproduction
A model behaves inconsistently in a specific multi-turn scenario. You export the problematic message array as JSON, share it in an issue tracker or forum, others can import it and replicate the problem.
Philosophical Classification
StatelessChatUI operates in a conceptual intermediate space:
Productive chat interfaces (ChatGPT, OpenWebUI) abstract the message array and focus on UX. State is implicitly managed, the user interacts with a chat surface, not with the underlying data structure.
Developer tools (Postman, API Playgrounds) expose the message array, but as a static request object. Each iteration requires manual rebuilding of the request.
StatelessChatUI combines both approaches: Chat interface with direct state access. You chat, but the message array remains manipulable at all times. This is neither “user-friendly abstraction” nor “developer tool”, but its own paradigm.
For productive work this is inefficient (too much overhead). For experimental work it is precise (maximum control without abstraction).
Conclusion
StatelessChatUI is a complementary tool for prompt engineering, API debugging, and teaching. It does not replace productive chat interfaces, but addresses workflows that are inefficient or impossible in these.
The central property: The message array is not a hidden backend artifact, but the primary work object. This enables systematic testing, precise debugging, and didactic exploration.
One HTML file. No installation. Complete API control. No persistence, no vendor lock-in.
For experimental work with LLM APIs: the most precise available tool.